Tonsil removal, or tonsillectomy, is a common surgical procedure often recommended for individuals suffering from chronic tonsillitis, sleep apnea, or recurring throat infections. It’s generally viewed as a permanent solution to recurring tonsil-related problems. But a question often lingers in the minds of many patients: Can Tonsils Grow Back After Being Removed? – Tymoff
The short answer is—yes, in some cases, tonsils can grow back, but it’s relatively rare. Understanding the reasons behind this phenomenon can offer peace of mind and help you stay informed about what happens post-surgery. In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind tonsil regrowth, potential symptoms, why it happens, and what you need to know if you suspect your tonsils are returning.
What Are Tonsils and Why Are They Removed?
Tonsils are two masses of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the throat. Their primary function is to help the immune system by trapping bacteria and viruses that enter through the mouth or nose. However, when tonsils become inflamed or infected frequently, they can do more harm than good.
Tonsillectomy is often recommended for individuals who experience:
- Chronic or recurrent tonsillitis
- Sleep apnea due to enlarged tonsils
- Difficulty swallowing because of swollen tonsils
- Persistent throat infections
In most cases, tonsil removal offers long-term relief from these issues. But does that mean you’ll never have to worry about your tonsils again?
Can Tonsils Grow Back After Removal?
Yes, tonsils can grow back, but it’s a rare occurrence. During a tonsillectomy, most of the tonsil tissue is removed, but in some cases, a small amount may be left behind. This residual tissue has the potential to regenerate, though it generally doesn’t grow back to the full size of the original tonsils.
However, this regrowth tends to be partial, meaning that while you may have some tonsil tissue, it’s usually not enough to cause the same problems as before. Still, for individuals who are particularly concerned about this, understanding how and why it happens can be crucial.
Why Does Tonsil Regrowth Happen?
Tonsil regrowth typically occurs when the surgeon leaves behind small portions of the tonsil tissue, which is often unavoidable during surgery. This is because removing every last cell is extremely difficult. While tonsil regrowth is not common, it can occur if the remaining tissue grows back over time. This process can take months or even years, but it’s often so slow that most people don’t even notice.
Factors that might contribute to tonsil regrowth include:
- Age: Children are more likely to experience tonsil regrowth compared to adults.
- Incomplete removal: If a small amount of tonsil tissue is left during surgery, it can regenerate.
- Healing process: The body may try to heal or regrow tissues as part of the normal healing process, though it’s usually minimal in the case of tonsils.
Symptoms of Tonsil Regrowth
It’s important to note that tonsil regrowth rarely causes the same severe symptoms that led to the initial tonsillectomy. However, if you suspect that your tonsils are growing back, you may notice some of the following symptoms:
- A feeling of fullness or obstruction at the back of the throat
- Mild soreness or discomfort in the throat
- Minor swelling at the site of the original tonsils
- The recurrence of throat infections, although not as severe as before
In most cases, if the tonsils do regrow, they tend to be much smaller and less problematic than the original enlarged tonsils.
What Should You Do If You Suspect Tonsil Regrowth?
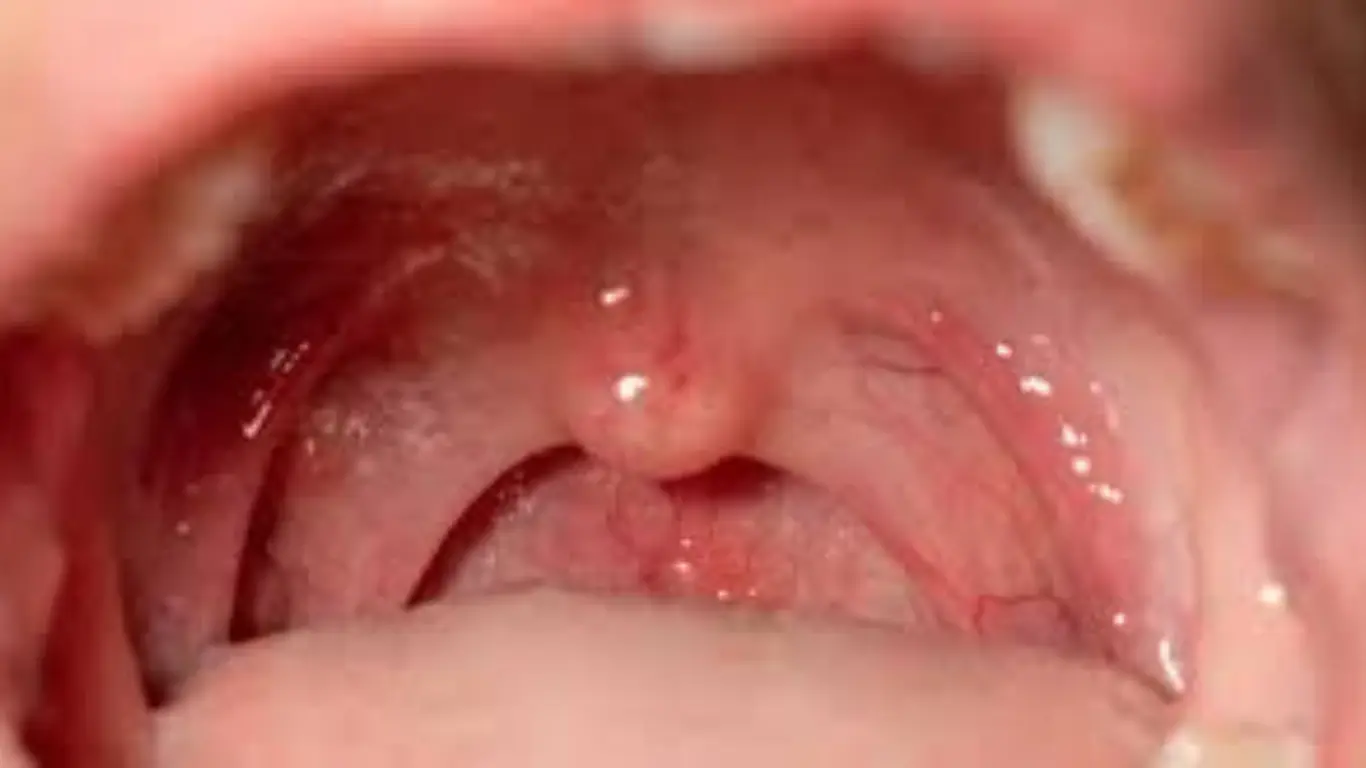
If you suspect that your tonsils are growing back, don’t panic. Tonsil regrowth is rarely serious and usually does not require another surgery. However, if you’re experiencing symptoms such as recurring throat infections, trouble swallowing, or sleep issues similar to what you faced before your tonsillectomy, it’s a good idea to consult your healthcare provider.
Your doctor can examine your throat to determine whether tonsil tissue is regrowing and, if necessary, recommend further action. In most cases, no additional treatment is needed unless the regrowth is causing significant problems.
How Common Is Tonsil Regrowth?
Tonsil regrowth is relatively rare. While exact statistics are difficult to come by, it’s estimated that less than 5% of individuals who undergo tonsillectomy experience significant regrowth. When tonsil tissue does regenerate, it is often small and asymptomatic.
Children may be more likely than adults to experience tonsil regrowth because their bodies are still growing and regenerating tissue at a faster rate. However, even in children, regrowth that causes notable symptoms is uncommon.
Tonsil Regrowth and Recurrent Infections: What You Should Know
One of the primary reasons individuals opt for a tonsillectomy is to avoid the recurrent infections that come with tonsillitis. In most cases, having your tonsils removed drastically reduces the frequency and severity of throat infections. However, some people may still experience sore throats or minor infections after surgery.
If your tonsils grow back, you might be concerned about a return of chronic infections. While this can happen, it’s rare, and the regrowth typically doesn’t lead to the same level of discomfort or illness. In cases where infection does recur, it’s more likely due to other factors such as:
- Exposure to bacteria or viruses
- Post-nasal drip or other throat irritants
- Allergies
If throat infections do return, it’s important to work with your doctor to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Preventing Tonsil Regrowth: Is It Possible?
Because tonsil regrowth is linked to residual tissue left behind after surgery, there’s little that can be done to completely prevent tonsil regrowth. That said, it’s important to have an experienced surgeon perform your tonsillectomy to minimize the chances of tissue being left behind. Follow-up care and regular checkups can also help monitor any signs of regrowth.
If you’ve had a tonsillectomy and want to avoid future issues, maintaining overall good health and hygiene practices—such as washing your hands frequently and staying hydrated—can help prevent throat infections, even if some tonsil tissue remains.
Will I Need Another Surgery if My Tonsils Grow Back?
In most cases, a second tonsillectomy is not necessary. Tonsil regrowth is generally minor and does not cause the same severity of issues that led to the initial surgery. However, in the rare case that regrowth leads to recurring infections, sleep apnea, or significant discomfort, your doctor may recommend another procedure.
The good news is that because regrowth is typically minimal, many people can manage their symptoms with conservative treatments such as antibiotics for infections or over-the-counter remedies for minor discomfort.
Tonsil Regrowth Is Rare but Manageable
The idea of tonsils growing back after being removed can be concerning, but it’s important to remember that this is a rare occurrence. In the unlikely event that your tonsils do grow back, it’s usually a partial regrowth that doesn’t cause the same problems as before.
If you do experience any discomfort or symptoms of regrowth, consult your healthcare provider for advice. Chances are, the issue can be managed without the need for additional surgery.
Overall, tonsillectomy remains an effective and long-lasting solution for those suffering from chronic throat infections, tonsillitis, or sleep-related issues due to enlarged tonsils.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can tonsils grow back after removal?
Yes, but it’s rare. Tonsil regrowth is generally minimal and unlikely to cause significant problems.
Why do tonsils grow back?
If small portions of tonsil tissue are left behind during surgery, they can regenerate over time. This happens more often in children than in adults.
How can I tell if my tonsils are growing back?
Symptoms of tonsil regrowth include minor throat discomfort, swelling, or a feeling of fullness in the throat. If you experience frequent infections, consult your doctor.
Is tonsil regrowth dangerous?
No, tonsil regrowth is rarely dangerous. Most cases don’t require treatment unless the regrowth is causing significant symptoms.
Can I prevent tonsils from growing back?
There’s no guaranteed way to prevent tonsil regrowth, but having an experienced surgeon perform the procedure and following post-surgical care instructions can minimize the risk.
Conclusion: Embrace Peace of Mind
While tonsil regrowth can happen, it’s a rare and usually minor issue. If you’ve had a tonsillectomy, the odds are in your favor that you’ll enjoy long-lasting relief from the symptoms that prompted the surgery in the first place. Even if your tonsils grow back, it’s unlikely to be a major concern. With proper care and consultation with your healthcare provider, any symptoms can be managed effectively, ensuring your long-term well-being.